
By 2026, explosionproof and ATEX VoIP Handsfree AI telephone solutions will be indispensable for ensuring safety and operational continuity in hazardous industrial environments. Evolving safety regulations, technological advancements, and the critical need for immediate, reliable communication in high-risk zones drive this necessity. The broader explosion-proof industrial telephone market, which often includes advanced VoIP Handsfree AI telephone systems, projects growth from USD 150 million in 2024 to USD 250 million by 2033. This growth highlights the increasing demand for robust communication tools like IP Fingerprint Visual Intercoms, railway intercoms, emergency help point call stations, and industrial video intercoms, all integrated within a reliable IP intercom system.
Key Takeaways
- By 2026, explosionproof VoIP Handsfree AI telephones will be very important for safety in dangerous industrial places.
- These special telephones help workers communicate clearly and safely, even in noisy or risky areas.
- AI in these phones helps with emergencies by understanding calls, making summaries, and finding exact locations.
- These phones are built strong to last in harsh conditions and meet strict safety rules like ATEX.
- They connect easily with other factory systems to make work safer and more efficient.
The Evolving Landscape of Hazardous Industrial Environments
Understanding Hazardous Zones and Inherent Dangers
Hazardous industrial environments present significant risks, demanding precise classification and robust safety measures. These areas classify based on the likelihood and duration of conditions where fire or explosion hazards exist. Flammable gases, vapors, combustible dust, or ignitable fibers define these conditions. North American installations use the Class/Division system, outlined by the National Electrical Code (NEC) and Canadian Electric Code (CEC). Internationally, and increasingly in North America, the Zone system is common. Both systems guide safety requirements for electrical equipment in explosive atmospheres.
| Class | Definition |
|---|---|
| Class I | Locations where flammable gases or vapors may be present. |
| Class II | Locations involving combustible dusts. |
| Class III | Locations where ignitable fibers are present in the atmosphere. |
The Zone system further refines these classifications:
| Gas | Dust | Hazardous Area Zone Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Zone 0 | Zone 20 | A hazardous atmosphere is highly likely to be present and may be present for long periods of time (>1000 hours per year) or even continuously |
| Zone 1 | Zone 21 | A hazardous atmosphere is possible but unlikely to be present for long periods of time (>10 <1000 hours per year) |
| Zone 2 | Zone 22 | A hazardous atmosphere is not likely to be present in normal operation or infrequently and for short periods of time (<10 hours per year) |
Beyond explosion risks, workers face various chemical hazards. These dangers include asphyxiants like hydrogen sulfide, corrosives such as sulfuric acid, and irritants like chlorine gas. Chemical exposure often leads to delayed health issues, including cancer, lung disease, or neurological damage years later. This delayed response means workers might unknowingly continue unsafe practices, accumulating harm over time.
Regulatory Imperatives: ATEX, IECEx, and Global Standards
Strict regulatory frameworks govern equipment and practices in hazardous environments. ATEX and IECEx are two prominent standards ensuring safety. ATEX, a European directive, is mandatory within the EU/EEA, focusing on equipment safety in explosive atmospheres. IECEx, an international certification scheme, offers global recognition and harmonizes standards worldwide.
| Feature | ATEX | IECEx |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | European directive, mandatory within the EU/EEA | International certification scheme, global recognition |
| Purpose | Ensures equipment safety in explosive atmospheres within the EU | Facilitates international trade by harmonizing standards globally |
| Compliance | Requires CE mark, Ex symbol, and Quality Assurance Notification (QAN) | Requires IECEx Certificate of Conformity (CoC) based on ExTR and QAR |
Beyond these, other critical standards exist. UL 121201 is required for US sites, alongside OSHA and insurance requirements. OSHA mandates that all electrical devices in classified areas must be certified by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL), such as UL or Intertek. Non-compliance can lead to legal action, site shutdowns, and financial penalties. Standards continuously evolve due to digitization and automation, with authorities collaborating to harmonize some standards while local laws and risks maintain differences.
The Cost of Failure: Safety Incidents and Downtime
Failing to comply with hazardous environment regulations carries severe financial and legal consequences. Companies face substantial fines and penalties, ranging from thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the severity and whether it is a repeat offense. Non-compliance often results in operational delays and shutdowns, leading to lost revenue and missed deadlines. For example, a trench collapse in construction leading to OSHA citations and a site shutdown resulted in $500,000 in direct and indirect losses.
The repercussions extend to increased insurance premiums, as a history of non-compliance elevates a business’s risk profile. Reputation damage also occurs, as public scrutiny and negative media attention erode customer trust and harm brand image. Legal fees and settlements from regulatory bodies or third parties can amount to millions. An unplanned outage in manufacturing due to an electrical injury halted operations for 48 hours, costing $350,000 in production losses and repairs. These incidents highlight the critical need for proactive safety measures and adherence to regulations.
The Rise of VoIP Handsfree AI Telephone in Safety Critical Applications
Why VoIP is Superior for Hazardous Zones
VoIP technology offers significant advantages for communication in hazardous industrial environments. It provides superior voice quality, even in noisy industrial settings, ensuring clear communication. This clarity is crucial when every word can impact safety. VoIP systems seamlessly integrate into existing communication infrastructure due to their compatibility with various VoIP platforms. This integration simplifies deployment and reduces the need for extensive new cabling.
VoIP also offers scalability, adapting to changing operational needs. It provides lower maintenance costs compared to traditional communication systems. Furthermore, VoIP integrates with unified communication platforms, enhancing overall operational efficiency. The ability to connect to Telco services using standard SIP VoIP offers options for digital PBX connections and integration with office phone systems. This technology improves audio quality by delivering ’4 wire’ without hum, noise, and loop loss when using VoIP dial tone providers. The flexibility of ubiquitous VoIP standards allows for various third-party hardware integrations. System components connect over standard IP/Ethernet networks, enabling multiple audio channels and control over a single RJ-45 jack. This connectivity provides potential cost savings by obtaining service through VoIP dial tone providers.
Handsfree Operation: Enhancing Worker Mobility and Safety
Handsfree operation significantly enhances worker mobility and safety in hazardous industrial environments. Hands-free voice and video calls improve communication between the field and the control room, particularly during inspections or emergencies. This capability allows workers to keep their hands free for critical tasks.
Wearables, such as headsets with embedded hands-free microphones, facilitate communication between workers without distraction. These devices are more convenient than traditional phones due to their small size, light weight, and comfortable attachment. Wearable devices also simplify information management by providing secure transmission, storage, and display of information, along with fast access to documents and notifications. Head-mounted, voice-controlled assisted reality devices offer true hands-free operation. They allow frontline workers to complete tasks safely and efficiently. These devices feature unmatched noise cancellation and voice recognition, enabling control with simple voice commands without needing to tap buttons. The micro-display is positioned below the line of sight and can move out of the way, preventing interference with vision or range of motion. A VoIP Handsfree AI telephone system leverages these capabilities to provide unparalleled safety.
The AI Advantage in Emergency Response
AI integration into handsfree telephones provides critical advantages for emergency response. Live transcription with automatic translation helps call takers understand callers who speak unfamiliar languages, are unclear, or speak too quickly. This feature allows real-time verification of information. AI also generates real-time incident summaries. It uses transcribed details to automatically create incident summaries within seconds, providing a clearer picture of the situation. Keyword detection enhances responder safety and supervisor oversight. The system listens for specific keywords, such as the presence of a weapon, and highlights them for immediate attention. It also alerts supervisors to critical calls, like CPR instructions for a child, ensuring proper protocol adherence and supporting call takers. Live video integration from callers provides situational awareness. This allows dispatchers to see what callers are experiencing, potentially catching details not verbally reported and enhancing officer safety.
AI analysis of audio for keywords or distress signals allows the system to prioritize urgent calls and automatically alert specific emergency services. For example, it can detect a medical emergency or security threat. Location-based services, powered by AI, pinpoint the exact location of the help point, guiding responders directly to the scene. AI-powered noise reduction algorithms filter out background noise, ensuring clear voice transmission, which is crucial in loud operational environments. Voice command functionality enables personnel to operate communication systems hands-free, initiating calls, sending messages, or accessing information using simple voice prompts. This advanced VoIP Handsfree AI telephone system significantly reduces emergency response times. AI uses predictive models to analyze continuous sensor data, identifying subtle deviations in pressure or temperature that precede crises. This provides earlier warnings than fixed alarms, distinguishing true hazard precursors from harmless variability. It leads to faster, more confident responses and gives critical time to intervene safely. AI dynamically recalculates optimum control limits in real-time by streaming sensor data through learning algorithms. This adapts boundaries as risk changes, preventing nuisance trips that stall production and ensuring operations stay within safe margins. AI studies historical event data to differentiate between process noise and emerging threats, reducing nuisance alerts that overwhelm staff. It clusters related alarms during upsets and ranks them by risk, cutting down alarm floods and allowing operators to react faster with sharper focus on critical safeguards. AI provides step-by-step guidance during emergencies by analyzing live process data and historical incident responses. It recommends effective response sequences, reducing cognitive load for operators, especially less experienced ones, and leading to faster emergency responses.
Key Features and Benefits of 2026 Explosionproof and ATEX VoIP Handsfree AI Telephone

Robustness and Durability for Extreme Conditions
Explosionproof and ATEX-certified telephones must withstand the harshest industrial environments. Manufacturers design these devices with specific materials and engineering principles to ensure their resilience. Robust enclosures contain internal explosions, preventing ignition of external hazardous atmospheres. Flame paths allow gases to escape safely while cooling. Effective heat dissipation designs prevent internal temperatures from reaching ignition points for surrounding gases or dust. Conduit sealing prevents the passage of flames or vapors through wiring systems.
Manufacturers select materials for their specific properties:
- Aluminum: This material offers lightweight construction, excellent thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. It efficiently dissipates heat.
- Stainless Steel: It provides exceptional strength and resists corrosion from chemicals and saltwater, ensuring durability in harsh conditions.
- Cast Iron: This material offers robustness and impact resistance. It absorbs and dissipates energy effectively during potential explosions.
- Non-Metallic Materials (Fiberglass Reinforced Polyester, Polycarbonate): These materials provide corrosion resistance, electrical insulation, and reduced weight. They perform well in corrosive environments.
- Sealing Materials (Silicone, Neoprene): These materials maintain explosion-proof integrity. They prevent the ingress of dust, moisture, and hazardous gases, offering flexibility and temperature resistance.
Rigorous certifications validate the robustness of these telephones. These include ATEX (Atmosphères Explosibles) Directive 2014/34/EU and IECEx, an international certification scheme. Other crucial standards include UL (Underwriters Laboratories), with UL 698 and UL 913 specifically for hazardous environments. Devices also often carry an IP65/IP67 rating for dust and water resistance and intrinsic safety certifications like IEC 60079-0. For instance, an ATEX Category 2 Marking like ATEX II 2G Ex ib IIC T4 (IECEx Gb) signifies compliance with stringent safety requirements.
Crystal-Clear Communication with Noise Cancellation
Clear communication is paramount in noisy industrial settings. Advanced noise cancellation technologies in explosionproof telephones significantly improve communication clarity. These systems achieve up to 30 dB noise reduction in targeted zones, allowing operators to communicate effectively despite high ambient noise levels. Damping and absorptive materials further reduce reverberation and echo, enhancing acoustic clarity in environments like steel mills.
AI-powered noise suppression offers measurable improvements in operational efficiency. It reduces average handle time (AHT) for communications, increases first call resolution (FCR), and boosts customer satisfaction (CSAT).
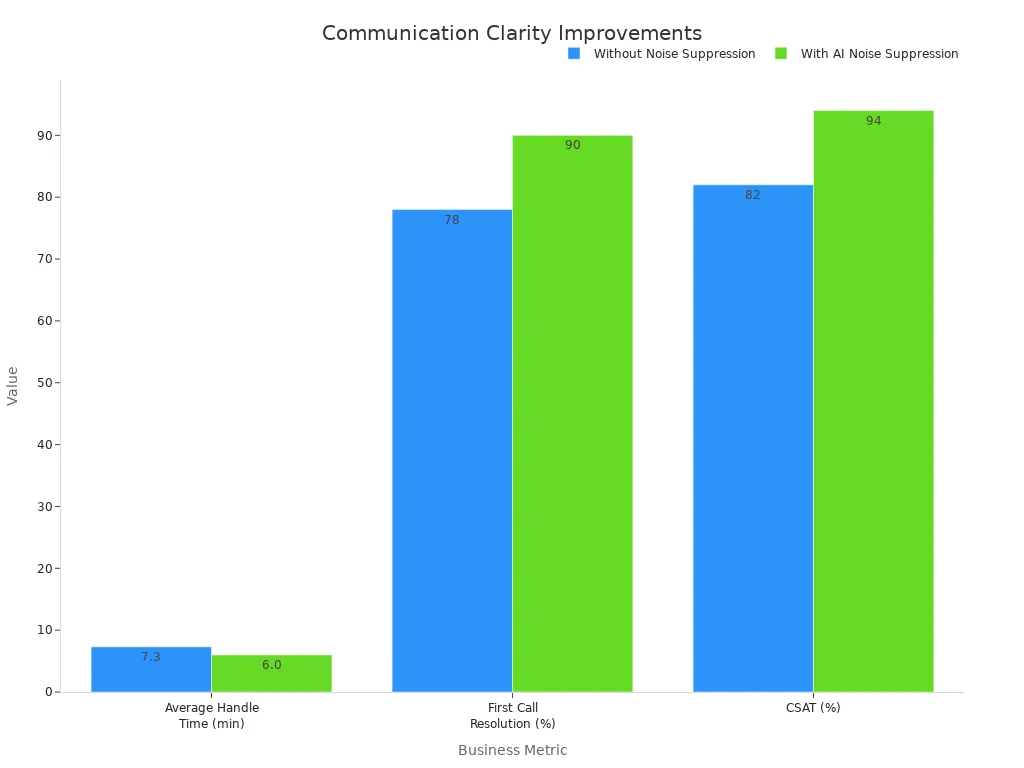
This chart illustrates the tangible benefits of AI noise suppression. It shows an 18% reduction in Average Handle Time, a 12% increase in First Call Resolution, and a 14% improvement in Customer Satisfaction. Such improvements directly translate to faster incident resolution and enhanced operational safety.
Seamless Integration with SCADA, PAGA, and IoT Systems
Modern industrial communication systems must integrate seamlessly with existing control and monitoring infrastructure. Explosionproof VoIP Handsfree AI telephone systems offer versatile integration capabilities with SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition), PAGA (Public Address and General Alarm), and IoT (Internet of Things) systems.
Integration methods include:
- Analog Integration: Telephones connect directly to analog ports on PAGA systems or use simple relays for alarm activation.
- VoIP/SIP: This digital method offers flexible connections to the facility’s network. It enables advanced features like automatic dialing and pre-recorded messages.
- Digital I/O Integration: This method employs simple on/off signals for direct system linking. An alarm system can activate an evacuation message, for example.
- Protocol Converters and Gateways: These act as translators between systems. They ensure unified communication when different protocols are in use.
- Centralized Control System Integration: A central system monitors and coordinates all safety devices. It provides a comprehensive overview and efficient emergency management.
Seamless integration offers numerous benefits:
- Higher Productivity: Integrated systems allow real-time communication between operators and machines. They optimize production schedules and minimize unplanned downtimes.
- Improved Decision-Making: Unified data systems provide consistent, actionable insights. Leaders make informed decisions based on trends and analytics.
- Cost Savings: Integrated systems eliminate redundant processes and deploy resources more effectively. They achieve significant cost efficiencies over time.
- Flexibility: A well-integrated environment adapts to new technologies or processes. This ensures the business remains competitive.
- Remote Monitoring and Diagnostics: This enables predictive maintenance and quick troubleshooting. It minimizes operational disruptions.
- Scalability and Flexibility: The systems support a wide range of devices and applications. They allow for adding new devices and functionalities as needed.
- Process Automation: Integration enhances process automation by providing real-time data and diagnostics. It optimizes production workflows and allows for precise adjustments and control.
- Reducing Human Error: Automation of repetitive and complex tasks minimizes human error risk. This increases reliability and enhances safety.
- Cost Efficiency: Integration lowers installation and maintenance costs by reducing extensive wiring and simplifying configuration. Predictive maintenance capabilities reduce unexpected breakdowns and repair costs.
Enhanced Security: Data Encryption and Network Protection
Explosionproof and ATEX-certified telephones operate in environments where communication integrity and data security are as critical as physical safety. Robust data encryption and network protection measures safeguard sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access or manipulation. These systems implement several advanced security features to ensure secure communication.
Explosionproof VoIP telephones support the SRTP encryption protocol, which secures voice communication. They also include an information verification mechanism, ensuring data authenticity. These systems utilize UDP, TCP, and TLS for transport, providing flexible and secure data transmission. A SIP trust server acts as an anti-attack mechanism, protecting against malicious intrusions. HTTPS certificate management secures web-based configurations. Configuration files also undergo encryption, adding another layer of protection. Furthermore, OpenVPN and IEEE802.1X protocols enhance network security and access control.
Industrial communication systems face various cybersecurity risks. Inadequate data validation in ICS software can lead to vulnerabilities such as buffer overflows, command injections, and cross-site scripting. Security features bundled with products often remain inactive by default, making them ineffective unless explicitly enabled. Communication and network configuration vulnerabilities also pose significant threats. These include unused data flows, which can lead to data exfiltration and unauthorized operations. Inadequate firewall and router logs make identifying the root cause of security incidents difficult. Plain text communication, common in standard protocols like Telnet, FTP, and HTTP, allows adversaries to eavesdrop, hijack sessions, and perform man-in-the-middle attacks. This exposes sensitive information like login credentials. Absent or incorrectly configured firewalls can lead to unrestricted data flow between networks, allowing malware to spread and unauthorized access. Many ICS protocols lack authentication, enabling data or device manipulation, replay attacks, and spoofing of sensors or user identities. Most industrial control protocols also lack built-in integrity checks, allowing tampering without detection. Insufficient authentication for wireless clients can permit connections to rogue access points or unauthorized access to ICS wireless networks.
The following table highlights common vulnerabilities in various industrial protocols:
| Protocol | Lack of Integrity | Lack of Confidentiality | Lack of Availability | Lack of Authentication | Lack of Authorization | Lack of Encryption |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNP3 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Modbus | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| IEC 60870-5-104 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| IEC 61850 | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| IEC 61400-25 | ✓ | |||||
| IEEE C37.118 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Mitigation principles address these cybersecurity issues. Confidentiality prevents unauthorized access to sensitive ICS information. Availability ensures the system maintains control to avoid economic losses. Integrity prevents disruptions caused by missing or corrupted data packets. Authorization and authentication mechanisms verify identity and prevent unauthorized privilege escalation and packet forgery.
Other potential cybersecurity risks include insecure passwords, integration of legacy systems lacking security, and inadequate management of vendor or third-party access. Poor firewalls and network segregation between ICS and wider organizational systems, along with internet connectivity of ICS/IoT devices, expose vulnerabilities. Irregular software updates and patch management, often due to concerns about production disruption, also create weaknesses. Non-encrypted communication and a lack of device authentication further compromise security.
Mitigation strategies address these risks comprehensively. Organizations review current security architecture and upgrade systems. They update passwords, enforce strong password policies, and consider changing factory-set credentials. Limiting privileged accounts, including third-party and vendor access, and enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) are crucial steps. Identifying and reviewing ICS network connectivity to non-ICS networks ensures firewalls, network segregation, transmission encryption, and access management are in place. Implementing network monitoring, event logging, alerting, and automated response solutions provides real-time threat detection. Reviewing potential cybersecurity gaps in new technologies and independently testing security controls are also vital. Assessing supplier cyber risk profiles and implementing mitigation or contingency plans strengthens the supply chain. Establishing incident response plans, training personnel, and conducting regular reviews and simulations prepare teams for potential breaches. Providing regular cybersecurity training and awareness programs for employees builds a strong security culture.
Common threats like malware, ransomware, phishing, insider threats, and supply chain vulnerabilities also target industrial systems. System weaknesses include outdated software, unpatched systems, and insecure remote access. Unsecured remote access for vendors and contractors can expose critical systems. Third-party components can introduce weaknesses if not properly overseen, including poor coding or outdated libraries in embedded systems.
Mitigation strategies for these threats include Privileged Access Management (PAM), which controls and monitors access for users with elevated privileges. Continuous monitoring and anomaly detection provide real-time visibility to detect threats and vulnerabilities quickly. Machine learning identifies deviations from normal system behavior. Robust remote access solutions, thorough security assessments of vendors, and enforced security standards via SLAs control third-party access. Supply chain integrity checks involve regular security audits and supplier assessments. Enforcing secure software development practices for suppliers and performing routine vulnerability scanning and penetration testing of third-party components are essential. Key security controls include network segmentation, MFA, patch management, data encryption, anomaly monitoring, firewalls, IDS, strict access controls, regular backups, and incident response plans. Best practices involve regular risk assessments, enforcing the principle of least privilege, timely patch management, using MFA, encrypting data, monitoring for anomalies, providing security training, establishing incident response plans, and auditing hardware and software. These comprehensive measures ensure the security and reliability of communication in hazardous industrial environments.
Global Demand and Market Trends for Explosionproof VoIP Handsfree AI Telephone by 2026
Geographic Hotspots Driving Adoption
Industrialized regions worldwide drive the adoption of explosionproof communication solutions. Areas with significant oil and gas operations, extensive mining activities, and large-scale chemical or power generation facilities show high demand. These regions prioritize worker safety and operational continuity. They invest in advanced communication systems to meet strict regulatory requirements. Global industrial hubs, particularly in Europe, North America, and Asia-Pacific, lead this market trend.
Industry Verticals with Highest Demand
Several industry verticals exhibit the highest demand for explosionproof communication. These include mining, steel plants, chemical plants, power plants, and oil and gas operations. These environments present unique communication challenges. For example, industrial settings often have high interference and physical obstructions. They require ultra-reliable wireless connectivity and fast roaming. Utilities face increasing demands, cybersecurity threats, and the need for resilient infrastructure. Across all these high-demand sectors, communication systems must handle high endpoint density during peak periods. They must also manage dynamic movement patterns and diverse data consumption needs. Stringent demands for security and support are also common.
Future Outlook: Innovations and Emerging Technologies
Future developments in explosionproof VoIP Handsfree AI telephone systems will integrate advanced technologies. AI integration transforms telephones into intelligent operational assets. These assets process data, automate tasks, and enhance decision-making. AI-powered noise reduction algorithms filter out background noise. This ensures clear voice transmission in loud operational settings. Voice command functionality allows hands-free operation of communication systems. Personnel can initiate calls, send messages, or access information using simple voice prompts. IoT-enabled connectivity will provide real-time monitoring and remote access. It will also integrate with building management systems. Innovations include non-contact activation through voice or proximity sensors. Built-in anti-bacterial coatings and self-cleaning surfaces will enhance hygiene. By 2025, modern systems will leverage AI to detect anomalies. They will automatically alert responders, projecting a 20% reduction in incident escalation.
Implementing Your 2026 Safety Solution: A Strategic Approach to VoIP Handsfree AI Telephone
Assessing Your Needs: Comprehensive Site Evaluation
Organizations must first conduct a thorough site evaluation. This step identifies specific communication challenges and safety risks within their hazardous environments. They assess the types of hazardous zones present. They also determine the potential for explosions or chemical exposure. This evaluation includes reviewing current communication infrastructure. It pinpoints any gaps in coverage or reliability. Understanding existing regulatory compliance requirements is also crucial. This comprehensive assessment forms the foundation for selecting the most appropriate safety solution. It ensures the chosen system meets all operational and safety demands.
Choosing the Right Provider: Key Considerations
Selecting a reliable provider is paramount for successful implementation. Companies should look for providers with extensive experience in industrial communication systems. The provider must offer products meeting international standards like ATEX, CE, FCC, RoHS, and ISO9001. A strong provider offers integrated services. These services include design, integration, installation, and ongoing technical support. They should also demonstrate in-house manufacturing capabilities for core components. This ensures quality control and dependable delivery. A provider with a global presence and a proven track record in diverse demanding environments, such as oil, gas, and tunnels, offers valuable expertise.
Training and Maintenance for Long-Term Reliability
Proper training and consistent maintenance are essential for the long-term reliability of any safety solution. All personnel using the new communication system require comprehensive training. This training covers system operation, emergency protocols, and basic troubleshooting. Regular maintenance schedules prevent unexpected failures. They ensure the system operates at peak performance. This includes routine inspections, software updates, and hardware checks. A responsive technical support team provides assistance when needed. This proactive approach guarantees the system remains a dependable safety asset for years to come.
By 2026, explosionproof and ATEX VoIP Handsfree AI telephone solutions represent a fundamental requirement. They move beyond mere upgrades. These advanced systems are crucial for operational safety and efficiency in hazardous industrial environments. Organizations must proactively adopt this technology. This ensures a safer, more connected future for all personnel. The VoIP Handsfree AI telephone integrates critical communication with intelligent response, making it indispensable.
FAQ
What is a VoIP Handsfree AI Telephone?
A VoIP Handsfree AI Telephone is an advanced communication device. It uses Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) for calls. It also integrates Artificial Intelligence (AI) for enhanced features. These features include noise cancellation and emergency response automation. It allows hands-free operation in hazardous environments.
Why are these telephones essential for hazardous industrial environments by 2026?
These telephones are crucial for safety and operational continuity. They meet evolving safety regulations. They also provide reliable, immediate communication in high-risk zones. Their explosionproof and ATEX certifications ensure safe operation.
How does AI enhance safety in these systems?
AI enhances safety through several features. It provides live transcription and real-time incident summaries. It also detects keywords and distress signals. AI-powered noise reduction ensures clear communication. It also guides responders to exact locations.
What certifications do Joiwo’s explosionproof telephones hold?
Joiwo’s explosionproof telephones hold numerous international certifications. These include ATEX, CE, FCC, RoHS, and ISO9001. They also have IP67 waterproof certification. These ensure compliance with global safety and quality standards.
Can these systems integrate with existing industrial control systems?
Yes, these systems offer seamless integration. They connect with SCADA, PAGA, and IoT systems. Integration methods include analog, VoIP/SIP, and digital I/O. This ensures unified communication and enhanced operational efficiency.
Post time: Jan-28-2026

