
Highways and tunnels present inherent dangers. Accidents, breakdowns, and other emergencies can occur unexpectedly. When conventional communication methods fail, an Emergency Help Point Call Station serves as a vital lifeline. These stations ensure people can quickly request assistance. Understanding the indispensable role of Emergency Help Point Call Stations in modern infrastructure is crucial. A Rugged Outdoor Emergency Telephone with Hands-Free SIP Intercom-JWAT416P Rugged Outdoor Emergency Telephone with Hands-Free SIP Intercom-JWAT416P Rugged Outdoor Emergency Telephone with Hands-Free SIP Intercom-JWAT416P Rugged Outdoor Emergency Telephone with Hands-Free SIP Intercom-JWAT416P Rugged Outdoor Emergency Telephone provides reliable communication. Similarly, a Public Emergency Call Intercom Telephone for Stations offers essential connectivity.
Key Takeaways
- Emergency Help Point Call Stations are very important for safety on highways and in tunnels. They help people get help fast when other phones do not work.
- Old emergency systems used simple ways to get help. New systems use advanced technology like fiber optics and smart sensors to find problems quickly.
- Modern emergency systems use new technology. This includes smartphones, strong monitoring tools, and fiber optic cables for reliable communication.
- These emergency systems work with traffic centers. They save money and can be used in many places, not just on roads.
- Future emergency systems will be even smarter. They will use new tech like AI and 5G to predict problems and make responses better.
The Evolving Landscape of Emergency Communication
Emergency communication systems have undergone significant transformations. They moved from basic methods to sophisticated digital networks. This evolution reflects a continuous effort to enhance safety and response times.
Traditional Emergency Help Point Systems
Historically, emergency communication relied on simple, direct methods. Early systems in the United States included church bells and messengers on horseback to alert communities. As technology advanced, the telegraph provided a nearly instant communication method. Later, radio communications, telephones, and sirens became common tools for emergency alerts. Roadside assistance also saw its own evolution. Emergency roadside call boxes on US highways allowed for simplified communication. Motorists could press color-coded options: blue for accidents or emergencies, green for broken-down vehicles, black for empty gas tanks or flat tires, and yellow to cancel requests. These traditional systems laid the groundwork for modern Emergency Help Point solutions.
The Rise of eCall and its Limitations
The European Union introduced eCall systems to further improve road safety. This regulation made eCall mandatory for new types of vehicles. It came into effect on March 31, 2018. All new vehicle types introduced to the EU market since then must have eCall. This led to rapid adoption. By 2023, over 90% of new cars sold in the EU were equipped with eCall systems. This marked a substantial increase from 50% in 2020. In Germany, a leading car manufacturer within the EU, more than 96% of newly registered passenger cars in 2024 featured a compliant eCall system. This indicates a high rate of adoption among local manufacturers.
Despite its widespread adoption, eCall has documented limitations. The system relies on circuit-switched 2G/3G communications. This can face challenges in maintaining continuous coverage, especially in tunnels. Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) are not obligated to inform highway operating companies about malfunctions, upgrades, or maintenance of their facilities. This can impact the reliability of eCall service in tunnels. Ensuring the continuity of 2G/3G/4G coverage in tunnels requires an appropriate monitoring infrastructure. This highlights a current limitation in guaranteeing service reliability in these critical areas.
Addressing Communication Gaps in Legacy Systems
Legacy emergency response systems often present significant communication gaps. Infrastructure limitations are common. Mobile networks or radio towers can become overloaded, damaged, or inoperable during large-scale events. This leads to breakdowns in coordination. Incompatible communication protocols also pose a challenge. Different emergency agencies, such as firefighters, police, EMS, and disaster management, often operate on incompatible systems. This hinders real-time information sharing and collaborative decision-making.
Furthermore, traditional alert systems are often generic and non-specific. They lack the ability to tailor messages based on geographic proximity, individual needs, or hazard type. This can cause confusion, panic, or non-compliance. Information silos and a lack of real-time data integration also limit situational awareness for first responders. Systems often operate in isolation, providing fragmented or outdated information. Finally, many emergency response frameworks are reactive. They rely on eyewitness reports or distress calls, which introduces critical delays in response time.
Upgrading these legacy systems requires strategic approaches. One effective strategy involves meticulous planning for legacy data migration. This includes assessing the scope, identifying critical data, and prioritizing tasks. Robust tools and methodologies streamline migration and minimize risks. Data cleansing and validation thoroughly rectify inconsistencies. Continuous monitoring addresses issues promptly. Integration with existing systems and workflows is also crucial. Identifying key integration points and understanding data exchange requirements helps. Defining interoperability standards ensures smooth communication. Middleware solutions and APIs facilitate data exchange. Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) or microservices can enhance flexibility and scalability.
Comprehensive training programs and clear communication channels are essential for change management. They keep users informed, address concerns, and solicit feedback. Cultivating a collaborative culture encourages open communication. Multi-channel communication, combining various platforms, ensures broad reach during crises. Integrating AI and machine learning enables automated responses and predictive analytics. IoT integration services provide real-time data from sensors and alarms, enhancing situational awareness. Custom solutions offer superior flexibility and scalability compared to off-the-shelf options. They facilitate the integration of advanced technologies, address industry-specific requirements, and ensure regulatory compliance. Leveraging cloud integration services guarantees system reliability and accessibility during critical events.
Advanced Technologies for Emergency Help Point Solutions

Modern infrastructure increasingly relies on advanced technologies to enhance safety and response capabilities. These innovations transform how people communicate during emergencies, making systems more accessible, efficient, and reliable.
Smartphone Integration for Enhanced Accessibility
Smartphones have become ubiquitous, offering a powerful platform for enhancing emergency communication. Integrating smartphone capabilities into emergency systems provides users with immediate access to assistance. People can use dedicated apps or web interfaces to report incidents, share their location, and receive critical updates. This integration significantly broadens the reach of an Emergency Help Point system.
However, integrating personal devices into emergency communication systems requires careful consideration of security and data privacy. Regulatory frameworks guide these considerations. HIPAA, for instance, mandates strict safeguards for patient information in healthcare settings, requiring encryption and access controls. FERPA protects student record privacy in education, necessitating secure systems that restrict access to student data. In the European Union, GDPR imposes stringent requirements on personal data processing, demanding strong data protection features like encryption and explicit consent for data usage.
Organizations implement best practices to ensure privacy and compliance. They select technology solutions with robust privacy features, including data encryption, access controls, and audit trails. Regular training educates staff on privacy regulations and the proper use of communication tools. Data minimization practices ensure systems collect and share only essential data during emergencies. Transparency with stakeholders about data usage and obtaining consent when necessary also builds trust.
Monitoring Infrastructure and Incident Detection
Advanced monitoring infrastructure plays a crucial role in detecting incidents quickly and accurately. These systems employ a variety of sensors and technologies to identify potential hazards in real-time. Piezoelectric transducers detect stress and strain in materials, converting mechanical stress into an electrical charge. Engineers use them in bridge monitoring and dam safety. Fiber optic sensors offer high sensitivity for measuring temperature, strain, and displacement. They operate effectively in electrically noisy and harsh environments, making them ideal for large structures like bridges and tunnels. Acoustic emission sensors detect early signs of material failure by listening to high-frequency stress waves. They provide insights into the internal conditions of concrete and steel, identifying damage in pressure vessels, pipelines, bridges, or dams. Electromagnetic sensors monitor corrosion and degradation of metallic structures by measuring changes in electromagnetic properties. They detect corrosion in reinforced concrete and steel.
Highway Tunnel Detection Systems (HTDS) represent integrated solutions designed specifically for tunnel environments. These systems incorporate sensors for detecting smoke, fire, and gas leaks, cameras for visual surveillance, and vehicle detection technologies. HTDS aims to enhance safety through early incident warnings, quick responses, and accident prevention. They also contribute to traffic flow management, congestion reduction, and overall tunnel efficiency. Implementation involves deploying hardware and software components, with sensors linked to centralized control centers for real-time data analysis. Many systems utilize AI and machine learning to identify anomalies and predict potential issues.
HTDS significantly improves incident detection and response. They identify smoke or fire within seconds, triggering alarms and alerting authorities. For example, sensor networks in a Singapore tunnel activate ventilation systems upon detection. Advanced sensors also monitor tunnel integrity for vibrations, cracks, or water ingress, while gas sensors track air quality. European tunnels, for instance, employ continuous structural health monitoring. AI-integrated cameras analyze footage for suspicious activity or unauthorized access, enhancing security in critical infrastructure like border crossings, as demonstrated by AI-enabled surveillance systems in Japan.
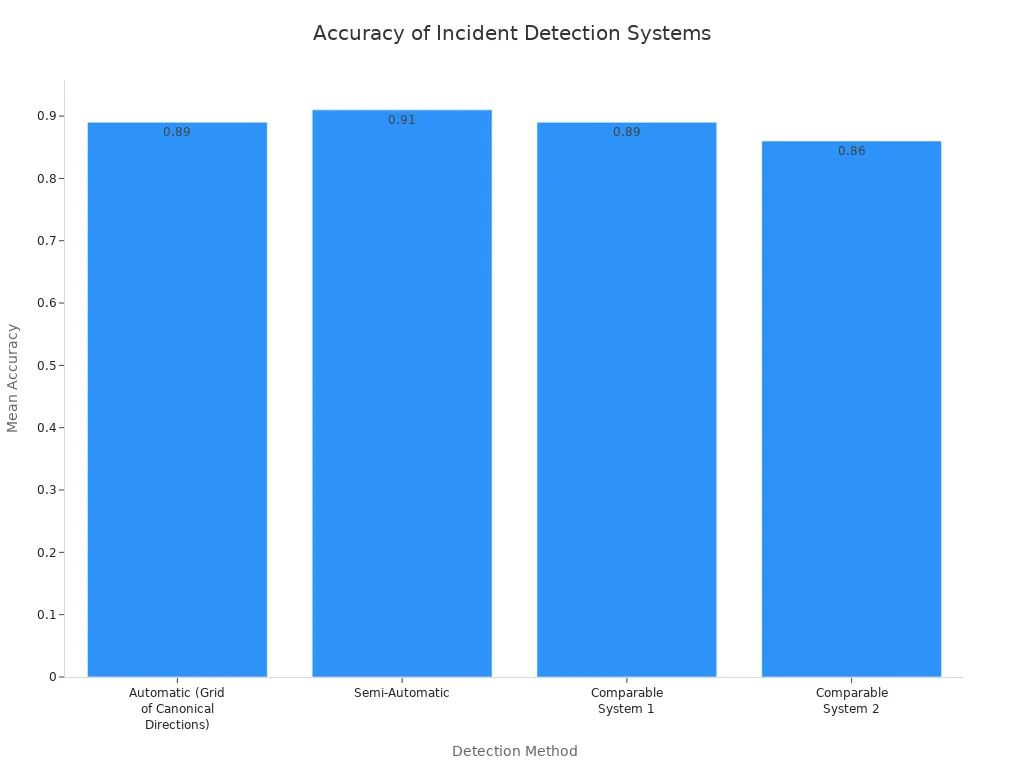
Automated incident detection systems demonstrate high accuracy rates. The table below illustrates typical mean accuracies for various detection methods:
| Detection Method | Mean Accuracy |
|---|---|
| Automatic (Grid of Canonical Directions) | 0.89±0.02 |
| Semi-Automatic | 0.91±0.03 |
| Comparable System 1 | 0.89 |
| Comparable System 2 | 0.86 |
Fiber Optic Communication for Reliable Emergency Help Point Networks
Fiber optic communication forms the backbone of reliable emergency networks. These cables offer significant advantages over traditional copper or wireless networks, ensuring robust and high-speed data transmission. Fiber optic cables provide superior speed, security, and durability, making them a crucial component of modern infrastructure.
Passive Optical Networks (PONs), utilizing fiber optics, are more economical to install and maintain compared to traditional copper networks. They deliver higher bandwidth, which is essential for applications like video streaming from surveillance cameras. PONs also offer greater reliability than copper networks because they are not susceptible to electrical interference.
Fiber optics provide significantly greater bandwidth than copper, crucial for data-intensive applications. Unlike copper, which experiences signal loss beyond 100 meters, fiber transmits data over miles without significant degradation. Fiber also resists electromagnetic interference (EMI), radio frequency interference (RFI), and temperature changes, ensuring high reliability. Improved security is another key benefit; fiber cables are difficult to tap into without detection, enhancing security for sensitive data. Furthermore, fiber networks offer future-proofing capabilities, supporting emerging technologies like 5G and AI, and providing a long-term solution for growing bandwidth needs.
Practical Implementation of Modern Emergency Help Point Systems

Modern infrastructure demands practical and efficient implementation of emergency communication solutions. These systems must integrate seamlessly with existing frameworks, offer clear advantages, and adapt to various environments.
Seamless Integration with Traffic Management Centers
Integrating emergency communication systems with Traffic Management Centers (TMCs) is crucial for coordinated incident response. This integration involves both technical and institutional efforts. Agencies often establish interagency agreements at the management level, as seen in Houston TranStar and Austin CTECC, to formalize cooperation and information sharing. Technically, TMC workstations gain full access to emergency data resources through connected networks or dedicated links. For instance, agencies use widely accepted standards like National Television System Committee (NTSC) and Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) for video exchange. Electronic data for traffic and incidents relies on processing and networking standards such as Ethernet, Structured Query Language (SQL), and Extensible Markup Language (XML). This allows for rapid and seamless data exchange between different computer-based systems. Regular interaction among agencies during localized emergencies also fosters strong working relationships, improving operational coordination.
Cost-Effectiveness and Operational Advantages
Modern Emergency Help Point systems offer significant cost-effectiveness and operational advantages. By streamlining communication and response protocols, these systems reduce the time and resources needed to manage incidents. Faster detection and intervention minimize potential damage, injuries, and traffic disruptions, leading to substantial savings. For example, automated incident detection systems, with their high accuracy rates, allow for quicker deployment of emergency services. This efficiency translates into lower operational costs for highway and tunnel authorities. Furthermore, the reliability of fiber optic networks reduces maintenance needs compared to traditional copper systems, contributing to long-term cost savings.
Broader Applications Beyond Highways and Tunnels
The utility of advanced emergency communication extends far beyond highways and tunnels. These robust systems find critical applications in diverse demanding environments. Industrial settings like oil and gas facilities, railways, and maritime vessels benefit from reliable communication in hazardous conditions. Public spaces such as hospitals, schools, and prisons also require immediate and secure emergency communication. For instance, an Emergency Help Point system can provide a vital link in a large hospital campus or a remote school building. Joiwo, for example, provides integrated communication systems for these varied sectors, including industrial telephones, explosion-proof telephones, and weatherproof telephones, ensuring safety across a wide range of critical infrastructure.
Designing and Deploying Robust Emergency Help Point Infrastructure
Effective emergency response relies on well-designed and strategically deployed infrastructure. Planners must consider various factors to ensure these systems function optimally when needed most. This involves careful planning from initial design to final implementation.
Key Considerations for System Placement and Design
Strategic placement of an Emergency Help Point system is paramount. Engineers position these stations for maximum visibility and accessibility. They consider factors like traffic flow, accident blackspots, and pedestrian access points. Power availability and network connectivity also dictate optimal locations. Designers ensure clear signage and intuitive user interfaces. They also account for potential obstructions and environmental conditions. The goal is to make the system easy to locate and operate during stressful situations.
Ensuring Durability and Reliability in Harsh Environments
Emergency communication equipment must withstand extreme conditions. Manufacturers use robust materials like stainless steel or reinforced plastics. These materials resist corrosion, impact, and vandalism. Products often carry high IP ratings, such as IP67, indicating protection against dust and water ingress. This ensures functionality in rain, snow, and high humidity. Equipment also tolerates wide temperature fluctuations, from freezing cold to intense heat. This commitment to durability guarantees reliable operation in tunnels, highways, and industrial settings.
Integrated Solutions for Comprehensive Safety
Modern emergency systems do not operate in isolation. They integrate with broader safety and communication networks. This includes connections to traffic management centers, public address systems, and surveillance cameras. Such integration allows for a coordinated response to incidents. For example, an activated help point can trigger nearby cameras and alert control room operators. This comprehensive approach enhances situational awareness and speeds up emergency services deployment. Joiwo provides integrated services for industrial communication systems, ensuring seamless operation across various critical infrastructures.
The Future of Emergency Help Point Technology
Emergency Help Point technology continues its rapid evolution. Innovations focus on faster, smarter, and more interconnected systems. These advancements promise to enhance safety and response capabilities significantly.
Continuous Innovation in Communication Systems
Communication systems for emergency help points are constantly improving. New technologies aim to provide more robust and efficient communication. These include:
- Advanced Computer Aided Dispatch (CAD) Systems: These systems share real-time data and track locations using GPS. They automate routing and provide critical information to responders.
- Drones and Small Cells: Drones with small cell technology can quickly deploy communication networks in disaster areas. They also provide real-time situation assessments.
- Virtual Reality (VR) for Training and Preparedness: VR creates immersive scenarios for emergency responder training. This enhances decision-making skills in high-pressure situations.
- Interoperability and Mesh Networks: IP-based networks and mesh networks allow seamless communication and data sharing among various agencies. This is especially useful when traditional infrastructure fails.
- Mobile Technology: Smartphones and disaster response apps enable real-time coordination and resource monitoring. They also instantly disseminate emergency warnings.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI uses advanced predictive analytics to forecast disaster trends. It prioritizes emergency calls and provides real-time translation services.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS captures geographical data for tracking and predicting disasters. This aids in improved resource allocation and planning.
- 5G Networks: 5G offers faster communication speeds and more reliable connectivity. It provides enhanced location services and supports AR/VR training. This increases resilience in emergency communication.
Predictive Analytics for Proactive Safety
Predictive analytics transforms emergency response from reactive to proactive. Systems analyze vast amounts of data to anticipate potential incidents. They collect data such as:
- Number of vehicles involved
- Involvement of pedestrians
- Number of injuries/fatalities
- Road type
- Crash location
- Date-time of crash
- Intersection type
- Presence of a nearby work zone
- Weather conditions
- Road surface conditions
Police crash reports provide factual information and police estimations. Naturalistic Driving Studies (NDS) monitor driver behavior and conditions directly. This data helps identify high-risk areas and conditions. Authorities can then implement preventative measures. This approach reduces accident frequency and severity.
Global Standards and Interoperability
Achieving global standards and interoperability is crucial for future emergency communication. Standardized protocols allow different systems and agencies to communicate seamlessly. This enables:
- Effective interagency cooperation.
- Management of emergencies throughout the entire lifecycle (preparation, response, recovery).
- Support for business-as-usual operations for emergency preparedness and critical infrastructure.
- Accelerated coordinated decision-making.
- Improved response outcomes.
These benefits highlight the importance of common frameworks. They ensure efficient and unified responses to emergencies worldwide.
Emergency Help Point Call Stations remain non-negotiable for modern road safety. They provide a critical lifeline when conventional communication fails. Continuous innovation ensures the relevance and effectiveness of these vital systems. Advanced technologies, like fiber optics and predictive analytics, enhance their capabilities. The future outlook for integrated emergency communication systems is promising. These systems will offer even greater safety and efficiency on highways and in tunnels.
FAQ
What is the main function of an Emergency Help Point Call Station?
Emergency Help Point Call Stations provide a critical communication link. They allow individuals to request assistance quickly during emergencies. This happens when conventional communication methods, like mobile phones, are unavailable or fail.
How does eCall compare to traditional Emergency Help Point systems?
eCall automatically dials emergency services after a serious accident. It transmits location data. Traditional systems require manual activation. They connect users directly to an operator for verbal communication.
Why is fiber optic communication essential for modern emergency networks?
Fiber optic communication offers superior speed, security, and durability. It transmits data over long distances without degradation. It also resists electromagnetic interference. This ensures reliable and high-bandwidth communication for emergency systems.
What types of environments benefit from Joiwo’s communication systems?
Joiwo’s communication systems serve diverse demanding environments. These include oil and gas facilities, tunnels, highways, railways, and maritime vessels. They also provide solutions for hospitals, schools, and prisons.
Post time: Jan-16-2026
